Signature
A signature is a unique way of identifying a person and confirming their commitment to a document or legal act. A signature not only spatially and substantively closes a document, but also completes the legal act itself.
A signature performs the following functions:
- a marking function – it allows you to mark/identify the person who performed a certain legal act,
- a declaratory function – confirms the content of the person's expression of will, expresses personal consent and testifies that the person agreed to the content of the document,
- a probative function – it confirms that the given expression of will was actually given.

Handwritten signature
It is a personal signature that is created by an individual directly with their hand or other limb. When writing a signature with their own hand, a pen, pencil or other writing instrument is used on paper or another substrate. The result of this writing is a signature on paper and usually includes names, surnames or other characteristic elements that allow the identification of the person.
Basic terms:
- Means for creating a signature: Hand, or limb.
- Result: Signature on paper (on another substrate).
Electronic signature
Legal regulation
The legal regulation of electronic signature can be found in several legal regulations, in particular in the following:
- Regulation (EU) No. 910/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the internal market (eIDAS Regulation) and repealing Directive 1999/93/ES.
- Act No. 272/2016 Coll. on trust services.
What is an electronic signature
It is data in electronic form that:
- is attached to or logically associated with other data in electronic form,
- which the signer uses to sign.
An electronic signature is designed to be technologically neutral, which means that it can be implemented in various ways. Regardless of the specific technology, it must always ensure that the signature is genuine (authenticity), the content of the document has not been altered (integrity) and the signer cannot deny having signed it (non-repudiation).
Requirements for the technical implementation of an electronic signature:
- Authenticity Recognition and unambiguous identification of the person signing a document at a specific time.
Integrity: Guaranteeing that the data has not been changed during the period from signing to signature verification. - Non-repudiation: Making it impossible for the signer to deny that he signed the document.
There are several technical solutions to achieve these goals, the most widely used ones being cryptography and the so-called digital signature.
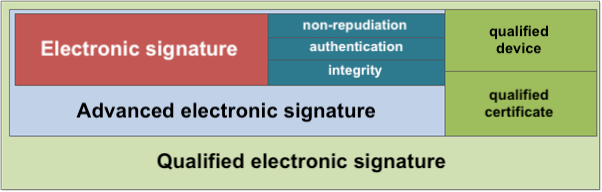
The eIDAS Regulation recognizes three types of signatures:
- “ordinary” electronic signature,
- advanced electronic signature,
- qualified electronic signature.
(Ordinary) Electronic Signature
These are data in electronic form that are attached or logically associated with other data in electronic form and that the signatory uses to sign. This type of signature can be implemented by signing an email message, a scanned signature or using dynamic biometric signatures.
Advanced electronic signature
According to the EIDAS Regulation, an enhanced electronic signature is an electronic signature that must meet additional requirements:
- Authenticity – recognition and unambiguous identification of the person signing a certain document at a specific time,
- Integrity – guaranteeing that the data has not been changed during the period from signing to signature verification,
- Non-repudiation – making it impossible for the signatory to deny that he signed the document.
All employees and doctoral students of Pavol Jozef Šafárik University in Košice who need it for their work are entitled to a certificate for an electronic signature. The manual for working with it can be found HERE.
Qualified Electronic Signature (QES)
According to the eIDAS Regulation, a qualified electronic signature is an advanced electronic signature that must additionally meet two requirements:
- is created using a qualified electronic signature creation device (e.g. eID),
- based on a qualified certificate for the electronic signature.