Strong passwords
- Passwords should be long enough – they should contain at least 12 characters
- They should be composed of a random sequence of alphanumeric characters
- They contain uppercase and lowercase letters and special characters (e.g.: +, ´, %, =, , \*, /,…)
- To make it easier to remember, it is advisable to create a password using a phrase (passphrase), e.g. Bear!jumps7over+Frozen>river
- Memory aid: a sentence in which you use only the first letter of each word (e.g.: The first apartment, in which I lived, was on Main Street 8. -> TfaiwIlwoMS8
Examples:
- correctHorseflashlightStitches
- I go to bed every day from 10 to 12.
- I g9 t9 b9d 9v9ry d9y fr9m 10 t9 12.
- ..71.plains.TRACK.sort.21..
- –42_party_WILL_signal_95–
- !!19=middle=FLOWERS=require=86!!

How does an attacker get passwords?
The security of your online accounts and sensitive information is crucial. It is important to understand the methods attackers use to get passwords and how to protect yourself from them.
- Dictionary attack: Attackers use lists of well-known words, common passwords and popular combinations to guess passwords. Therefore, it is important to:
- Use a random combination of characters, numbers and symbols.
- Have a complex password with a variety of characters found in dictionaries
- Brute force attack: Attackers use special programs to automatically generate and test a huge number of possible passwords. The longer and more complex the password, the more resistant it is.
- Social engineering: Attackers use not only technology, but also manipulation and psychology to get passwords. They can impersonate trusted people, use phishing or manipulate through communication (see the Social Engineering module).
Avoid these password creation approaches
- Strings with repeated characters or well-known combinations: Using simple strings that contain repeated characters, such as "123456", "222222", or "abcdefg", is extremely dangerous because they are easy to guess and susceptible to brute force attacks.
- Dictionary words: Avoid using simple dictionary words like "password", "elephant", "secret", as attackers can use dictionary attacks to guess your password. Better solution: Use random words combined with special characters and numbers (e.g. "Slnk0#Líška!97").
- Personal information: Do not use your personal information, such as your first name, last name, nickname, login name, or date of birth, as part of your password, as this information is often publicly available and easily discovered by attackers. Use a combination that has no connection to your personal information.
How to protect yourself?
Use a different password for each account
It is important to have a unique password for each online service or account. If you use the same password in multiple places and one of them is compromised, your other accounts may also be at risk. Therefore, it is recommended to have a unique and complex password for each account.
Passwords should be completely different. If an attacker gets one of your passwords, they often try modifications of the password to log in to your other accounts. For example, “stolicka.5okno” and “stolicka.5okno1” are different passwords, but the second password could be easily guessed.
Don't write your passwords down in visible places
Don't write your passwords down on a piece of paper, on your monitor screen, on your keyboard, or in your calendar. These places are vulnerable to unauthorized access and can compromise your security.
Do not store passwords in unencrypted documents on your computer
If someone gains access to your device, unencrypted password files could lead to sensitive data being leaked.
Periodically check if your passwords have been compromised in a data breach
An example of a site where you can check is: https://haveibeenpwned.com/ https://haveibeenpwned.com/
This site allows you to see if your data has been compromised in a known data breach. If so, it is important to change your passwords on all services where the same password is used. You can set up an alert to send you a notification if you find yourself in a breach.
Other similar sites are:
Use a password manager
Programy ako Bitwarden a KeyPass vám umožňujú bezpečne uchovávať heslá a generovať silné kombinácie. Stačí si zapamätať jediné (hlavné) heslo.
- This method is suitable for use on different devices, such as computers and mobile phones. This allows you to access your passwords from any device.
- This way you can be sure that your passwords are stored securely and only accessible to you.
Don’t save passwords in web browsers
Passwords stored in your browser are often less secure than in dedicated password managers. Browsers don’t have the same levels of encryption and data protection as password managers. The passwords that your browser remembers are often stored in a database directly on your device. If someone gains access to your computer or device, they can easily find and exploit your saved passwords. Some browsers may send your saved passwords to the cloud, which poses an additional security risk to your passwords.
Don't use similar variations of passwords
These are passwords like "stolicka.5okno" and "stolicka.5okno1". Attackers test modifications of a leaked password. This way they could figure out the other one from one leaked password.
To check the strength of your password, you can use our password tester, which is located on our website https://csirt.upjs.sk/hesla/. It provides information on how long it would take a computer to guess your password, how vulnerable the individual components of your password are, and which of the basic password creation rules were not met.
Multifactor Authentication
Today, we store a lot of sensitive data in our online accounts. Password protection alone – even if strong – may not be enough. It is a good idea to use multi-factor authentication (MFA), which increases the security of your account.
This is the process of verifying a user’s identity using multiple categories of factors. Combining more than one authentication method minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
Multi-factor authentication means using multiple authentication methods/factors to verify a user’s identity..
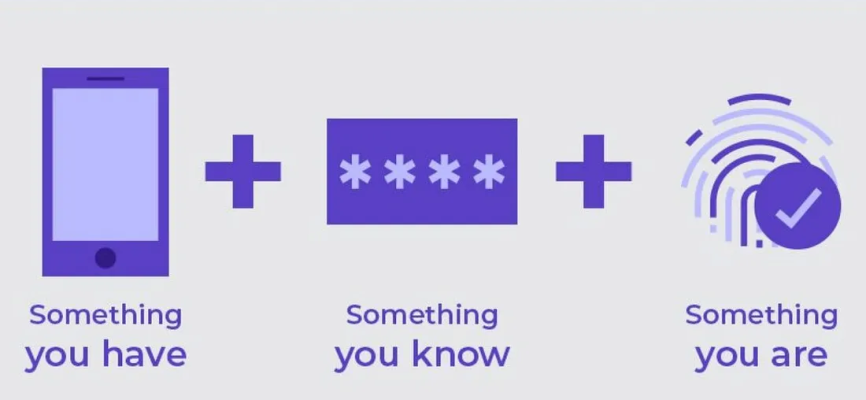
There are three basic categories of factors:
- Something I am: This factor focuses on the user’s unique physical characteristics. This includes their fingerprint or facial recognition using technologies like Face ID.
- Something I have: This factor refers to physical objects the user owns. This could be a card, smartphone, or other device used for authentication.
- Something I know: Ide o faktor založený na znalostiach. Sem patrí PIN kód alebo heslo, ktoré si používateľ zapamätá. Viacfaktorové overovanie kombinuje viacero autentifikačných faktorov – zväčša heslo (niečo, čo viem) a nejaký druhý faktor.
The primary factor is often a password (the “something I know” factor), which is supplemented by another factor. This second factor can be, for example:
- SMS code: The user receives a code via SMS to their phone.
- App code: The app generates a one-time code that the user enters when logging in.
- Notification confirmation: The user receives a notification on their phone and confirms it as a part of the verification.
- Hardware key: A physical key (for example a YubiKey) is plugged into the device and confirms the verification.
These additional factors increase security by requiring an attacker to have more than just a password to gain access. It is recommended to enable multi-factor authentication whenever possible to verify that the person logging into your account is really you.
Why should you use multi-factor authentication?
- Increases account security – Útočník potrebuje viac ako len heslo na získanie prístupu.
- Protects against phishing – Even if an attacker gets your password, they won’t be able to log in without a second factor.
Enabling multi-factor authentication significantly increases the security of your online accounts and protects your sensitive data from unauthorized access. It is recommended to enable MFA wherever possible, but at least on important accounts such as email, online banking, or password managers.