There are several terms that are essential for a proper understanding of the relationships within information security. In this document, we present a selection of such concepts, in addition to those already explained in other topics of this course.
Note: Words highlighted in blue refer to other terms explained within this document.
Asset
It refers to everything that has some value to us and therefore requires protection. Examples of assets are computers, personal data, important internal documents, employees, etc. The goal of information security is to secure the assets of information systems, companies, etc.
Service pack
A collection (package) of multiple updates that can be installed at once.
Algorithm
A sequence of steps which lead to the solution of a given problem/task. (e.g., a cake recipe is also an algorithm).
Antivirus / Antivirus software
A program that performs one or more of the following functions: scanning for malware (using one or more different techniques, often with the option to select them or set the scan mode), cleaning infected files, backing up and restoring system partitions on a disk, storing file control information on a disk, providing information about viruses, etc.
Authentication
The process of verifying the user's identity.
Credentials
Data that is transmitted to determine the declared identity of a given entity. In other words, it is data that serves to verify that someone is who they claim to be.
Authorization
Granting rights, which involves granting access based on the subject's access rights. Granting access is necessary to perform certain activities in the information system or to access data. It occurs after successful authentication.
Security incident
An event that compromises or potentially compromises the confidentiality, integrity or availability of an information system or the information that the system processes, stores or transmits, or that represents a violation or imminent threat of a violation of security policies, security guidelines or standard security operating rules.
Contacts for reporting a security incident at UPJŠ are published on the official website csirt.upjs.sk.
Biometric
It refers to the use of specific attributes that reflect unique biophysiological characteristics, such as a fingerprint or voiceprint, to verify a person's identity.
Recovery point objective (RPO)
The point in time by which data must be restored after a failure.
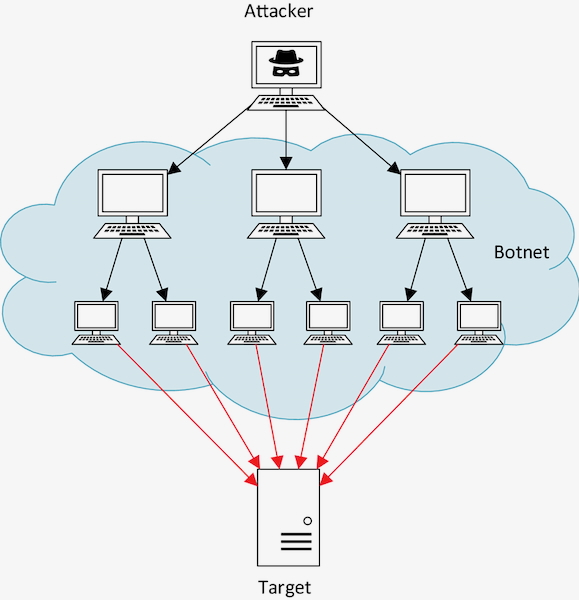
Botnet
Network of infected computers controlled by a single device that has access to their computing power. It enables widespread illegal activity – particularly DDoS attacks and spamming.
CAPTCHA
A computer program or system designed to distinguish human input from a machine one, usually as a way to prevent spam and automated data extraction from websites.
Certification authority
In the field of cybersecurity it is a third party that issues digital certificates and uses its authority to confirm the authenticity of data that exists in the freely accessible part of the certificate.
Certification
In cybersecurity a process by which a third party provides assurance that an entire data processing system or part of it meets security requirements. The process of verifying the capability of communication and information systems to work with classified information, approving this capability, and issuing a certificate.
Cookie
Data that a web application can store on the computer of a logged-in user. The browser then automatically sends this data to the application each time it is accessed. Cookies are most commonly used today to recognize users who have previously visited the application or to store user settings for the website. Today, they are often discussed in connection with tracking user activity and behaviour on certain websites.
Creative commons (CC)
A non-profit organization based in Mountain View, California, United States, dedicated to expanding the range of creative works available for others to legally create and share. The organization has released several copyright licenses known as Creative Commons licenses, which are free to the public.
Dark web
This is a part of the internet that is not visible to regular search engines (e.g. Google). It provides greater anonymity and is therefore used for various purposes – from privacy protection to illegal activities such as selling drugs, login details or ordering hacking services.
Database
A set of structured data that describes data properties and relationships between corresponding entities (records).
Data center
A data center is a facility used to house computer systems and related components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. It generally includes backup power supplies, redundant data communication links, environmental controls (e.g., air conditioning, fire suppression), and various security devices.
Domain name
A name used to identify a computer, device, or service on a network (including the Internet). Often, the abbreviated term domain is used. Example of a domain name: www.abcdefgh.sk.
Impact
The consequences of an act or an event. In cybersecurity impact refers to how a cyber attack or an incident can affect the security of information or systems. For example, a successful attack can lead to compromization of sensitive data or weakened overall cyber defenses.
Availability
The characteristic of being accessible and usable at the request of an authorized entity.
Confidentiality
The characteristic that information is not accessible or made available to unauthorized persons, entities or processes.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response)
Security technology that monitors, detects and responds to threats on endpoints (e.g., computers, servers) in real time. Unlike conventional antivirus, EDR also analyzes unknown and advanced attacks and allows for a quick response to security incidents.
Electronic mail (E-mail)
It is a form of digital communication that allows messages to be sent and received via computer networks, most commonly the Internet.
End-to-end encryption
The goal is to protect the content of your communication by encrypting messages directly on your device and allowing only the recipient to decrypt them - no one else, not even the service provider, has access to them.
Exploitation
The process of exploiting a vulnerability.
Firewall
A comprehensive system of security measures designed to prevent unauthorized electronic access to a computer or specific services on a network. Also a system of devices or a collection of devices that could be configured to allow, deny, encrypt, decrypt, or act as a proxy for all computer communication between different security domains based on a set of rules and other criteria. Firewall can be implemented as hardware or software , or as a combination of both.
Forensic analysis/investigation
Analysis of digital data to obtain evidence of users' (attackers') activities in the field of information and communication technologies.
Hardware
Physical system components (devices) or parts of a system (e.g. computer, printer, peripheral device).
Hash functions
This is a one-way mathematical transformation of input data (text) into a file (fingerprint, hash). From a computational point of view, it is practically unrealistic to recover the original data from the returned hash. This function is used in data security applications (e.g. authentification, digital signature, integrity check).
Hacker
The term hacker is often equated with the term attacker. In fact, a hacker is one of the categories of attackers who has sufficient knowledge, skills, and tools to carry out Attack vector.
Hacktivists
They are similar to hackers. However, they differ in the specific goals of their attacks. For example, environmental protection, protection of cryptocurrencies, etc.
Honeypot
Honeypot is a trap for attackers. It is a fake system or network that pretends to be a real target. It can exist inside a real computer network or in isolation outside it. A honeypot can contain vulnerabilitieswhich seem attractive to attackers. In fact, all activity on this network is monitored and recorded.
Threat
A threat is a potential cause of an undesirable incidentthat can compromise the security of a system or organization and cause damage. It is any factor capable of acting against an asset in such a way that it can be damaged. Examples of threats include fire, malicious code, data leakage, destruction of documentation, phishing, spam and other security risks.
Identification
The act or process by which an entities represents an identifier to the system by which the system can recognize the entity and distinguish it from other entities.
Identity
A set of characteristics that uniquely identify a specific object – a thing, a person, an event.
Incident
In ICT (Information and Communication Technology) it is an eventthat is usually associated with a network or service failure or deterioration in their quality.
Information
Any symbolic expression that has meaning for the communicator and the receiver.
Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
Information and communication technologies mean all technologies dealing with the processing and transmission of information, especially computer and communication technologies and software.
Information system
A functional unit enabling purposeful and systematic information acquisition, processing, storage and access to information and data. It includes data and information sources, media, hardware, software and tools, technologies and procedures, related standards and employees.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
In cryptography, this refers to the infrastructure for managing and distributing public keys from asymmetric cryptography. Through trust transfer PKI allows the use of unknown public keys to verify an electronic signature without having to verify each one individually. Trust transfer can be implemented either through certification authority or via a trusted network (e.g. PGP).
Insider
Category of attackers, which is the user themselves within the organization.
Integrity
Protection against improper modification or destruction of information, which includes ensuring the non-repudiation, completeness, accuracy and authenticity of information.
IP address (Internet Protocol Address)
A unique numerical identifier assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address allows the location and identification of a device within a computer network.
Users can find out their IP address using services such as whatismyip.com.
IP spoofing
Spoofing the source IP address of the device (computer) initiating the connection (with the recipient) in order to conceal the real sender. This technique is primarily used in DoS attacks.
To be compromised
A breach of information security that may lead to damage to a program or data, its modification, destruction or disclosure to unauthorized entities.
Communication system
A system that ensures the transmission of information between end users. It includes end communication devices, transmission environment, system management, personnel handling, and operating conditions and procedures.
Critical infrastructure
Systems and services whose failure or malfunction would have a serious impact on the security of the state, its economy, public administration, and ultimately on ensuring the basic daily needs of the population.
Cryptography
A discipline that encompasses the principles, means, and methods of transforming data in order to hide its semantic content, prevent its unauthorized use, or prevent its undetected modification.
Cybersecurity
A set of legal, organizational, technological and educational means aimed at ensuring the protection of cyberspace.
Cybercriminality
Criminal activity in which a computer appears in some way as a collection of technical and software equipment (including data) as the object of interest of this criminal activity (with the exception of such criminal activities whose object is the described devices considered as immovable property) or as an environment (object) or as an instrument of the criminal activity.
Cyber warfare
The use of computers and the Internet to wage war in cyberspace. A system of large-scale, often politically motivated, interconnected, and mutually provoked organized cyber attacks and counterattacks.
Cyberspace
A digital environment enabling the creation, processing and exchange of information, made up of information systems, information services and electronic communications networks.
Cyber attack
Attack on an IT infrastructure with the aim of causing damage and obtaining sensitive or strategically important information. It is most often used in the context of politically or militarily motivated attacks.
License
Permission and the document that records this permission.
Malware
This is a general term for malicious programs. Malicious software includes computer viruses, Trojan horses, worms, spyware, and so on.
Monitoring
Determining the state of a system, process, or activity. Inspection, surveillance, or critical observation may be required to determine the state.
National authority
State body responsible for questions and issues related to cybersecurity issues.
Undeniability
The ability to prove the occurrence of a declared event or activity and its perpetrators.
Data recovery/data restoration
The act of restoring or recovering data that has been lost or had its integritycompromised. Methods include copying data from an archive, reconstructing data from source data, or restoring data from alternative sources.
Denial of Service (DoS)
Risk assessment
The process of comparing the results of a risk analysis with risk criteria to determine whether the risk and/or its magnitude is acceptable or tolerable.
Vulnerability assessment
The process of identifying, quantifying, and prioritizing (or ranking) vulnerabilities in a system.
Operating system (OS)
Softwarethat controls the execution of programs and can provide various services, such as device allocation, scheduling, input/output control, and data management. Examples of operating systems include Microsoft Windows, MS DOS, LINUX, UNIX, Solaris, and others.
Penetration testing
It is a process that simulates real-world cyber attacks to identify vulnerabilities in systems, applications, or networks. The goal is to verify the level of security, uncover weak points, and provide recommendations for their removal.
Computer security
The branch of computer science focused on protecting computer systems, networks, data, and digital devices from unauthorized access, misuse, damage, or theft. It includes technologies and processes that protect digital assets and ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information.
Service provider
Any physical or legal person who provides any of the company's information services.
Intrusion
Unauthorized access to a computer system, network, or service.
Zero Trust Principle
This is a security model that is based on the assumption that no person or device should be automatically trusted. Every
connection is considered untrusted until it is verified. This principle implements, for example, rigorous identityverification or limiting access to all users to the minimum necessary.
Access rights
Authorizing a subject to access a specific object for a specific type of operation.
Countermeasure
Any activity (e.g. training), technology (e.g. firewall), or process (e.g. access control) that partially or completely protects assets or a subset of assets from specific threats.
Access control
It is a set of policies, processes, and technologies that ensure that only authorized individuals or systems have limited and controlled access to information assets (e.g., data, applications, systems) based on business and security requirements.
Risk
The probability that a given value (asset) will be destroyed or damaged (impact) by a specific security threatsthat acts on the weak side of this value is called risk. An example in the case of an attack – a phishing campaign – is the probability of revealing employee access data to the organization's systems (e.g. to an email account).
Role
A summary of specified activities and necessary permissions for entities operating in an information or communication system.
SIEM (Security Information and Event Management)
SIEM is a security tool that centrally collects, analyzes, and evaluates data from various IT systems in real time. It enables threat detection and provides an overview of security events in one place.
Network
A set of computer terminals (workstations) and servers that are connected so that they can exchange data with each other and communicate with each other.
Script
A set of instructions written in a specific formal language that controls the operation of a device, program, or system.
Skript kiddies
People who are not experienced hackers. They use tools available on the Internet to carry out malicious activities without a deep understanding of how they work.
SOC (Security Operations Center) team
Software
A set of programs used on a computer that perform data processing or other specific tasks.
Spam
Unsolicited messages, such as advertisements or others, usually of a commercial nature, that is distributed on the Internet.
Subject
In cybersecurity it is an active entity that can access objects.
Log file
A file containing information about the activities of subjects in the system. Access to this file is controlled.
File system
A method of organizing and storing data in the form of files so that it can be easily accessed.
System Administrator
A person responsible for the administration and maintenance of a computer system.
Computer security incident response team - CSIRT
CSIRT is a team of information security experts who detect, analyze, and resolve security incidents and assist in system recovery. In addition to reactive services, they also provide prevention and education, inform about vulnerabilities and propose measures to eliminate them.
Computer emergency response team - CERT
Event
The occurrence or change of a particular set of circumstances.
URL
The address of a website.
Attacker
An individual, group, organization, or government that conducts or intends to conduct malicious activities.
Attack
It is the intentional or unintentional exploitation of vulnerabilities with the aim of causing damage, loss or disruption to assets (e.g. data, systems or services). It includes any malicious activity that attempts to collect, disrupt, degrade, destroy or deny access to information systems and their resources.
User
Any natural or legal person who uses an information society service to search for or access information.
Attack vector
Overloading
Accidental or intentional injection of a large amount of data that results in a denial of service.
Patch
An update that corrects a security problem or unstable behavior of an application, extends its capabilities, or improves its performance.
Exploit
A bug or error in a program, software, sequence of commands, or code that allows a user to use programs, computers, or systems in an unexpected or unauthorized way. Also known as a security hole or exploit.
Zombie
An infected computer that is part of a network of controlled devices (botnet).
Vulnerability
A term used in risk management to refer to a weakness or deficiency (assets). A vulnerability allows a threat to be exploited. In risk analysis, a vulnerability is a property of an asset.